Contents
Digital-only banks have been steadily gaining traction, particularly after the pandemic. They are also known as online banks, neobanks, digital challenger banks, internet-only banks, and virtual banks. So what makes them different, and what to expect from this new type of bank?
Digital-only banks: The revolution
The primary distinction between neobanks and traditional banks is that the former is entirely digital. A digital-only bank offers financial services only via digital devices such as mobile phones, tablets, and the Internet. With electronic documentation, real-time data, and automated procedures, neobanks introduce a simple way to streamline baking activities, giving them an advantage of convenience over traditional banks.
Digital-only banks, managed by FinTech companies, follow the “Banking as a Service” model and offer debit cards and extensive banking services via mobile apps without any physical branch. Unlike traditional banks, they are not burdened by legacy IT infrastructure, which is difficult and expensive to operate. These banks use cloud-based technology rather than on-premise infrastructure. Customers are handled under a more straightforward process and not limited to traditional working hours like physical banks.
Besides, personalization is yet another distinctive feature when it comes to neobanks. Digital-only banks use “Real-time intelligence” to give personalized customer information such as expenditure alerts, geo-based offerings, and warnings about customers’ spending habits, especially when particular purchases are likely to exceed their budgets. Such individualized services will improve customers’ experience and practically benefit customers’ financial status, and, as a result, increase customer loyalty over time.

Another difference between digital-only banks and traditional ones lies in the way they secure customers’ information. Thanks to their innovative technology, neobanks can implement such solutions as biometric-based service offerings. Atom Bank, for instance, is based on the FIS platform that enables biometric security and an in-app account opening tool to keep ahead of the competition. Customers trust authentication methods such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice recognition because these traits are unique to each individual. Thus, customers can save time identifying themselves and be guaranteed a secured login.
On the other hand, traditional banks may still require a physical presence for customer identification in certain transactions, from as simple as account opening to mortgage, depending on the regulations. This is partly because the working process of traditional banks has been followed for years, so it’s harder for them to adopt the latest technologies, which may lead to significant changes in the whole system.
The rise of digital-only banks
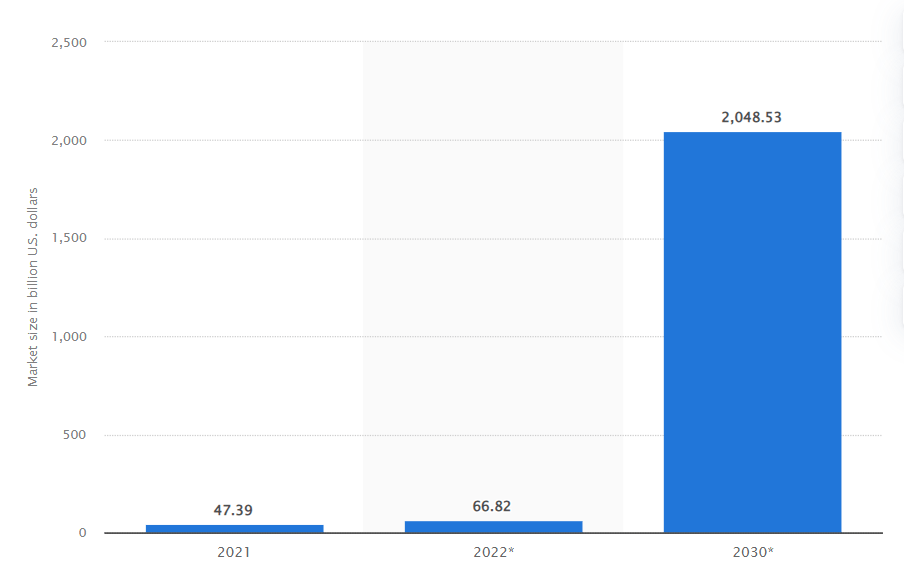
In 2020, the market for digital-only banks was expected to be worth roughly 35 billion dollars. Estimations predicted that the sector’s market size would increase at a CAGR of 47.7% through 2028, reaching a value of 722.6 billion US dollars.
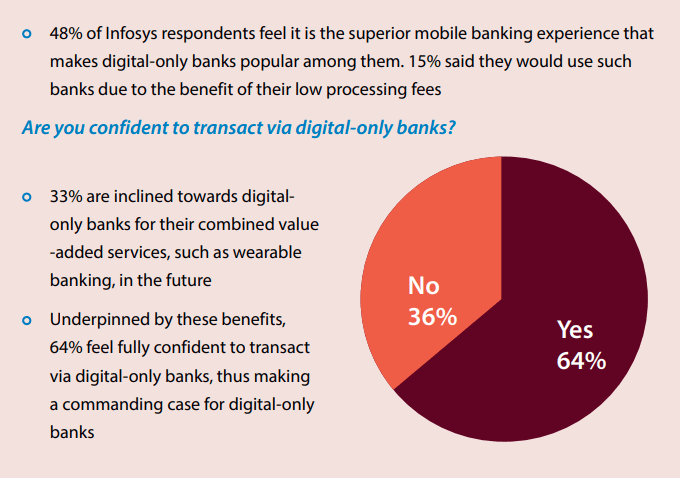
According to a survey of Infosys on bank users, digital-only banks are popular with respondents because of 2 main reasons: an enhanced mobile banking experience (48%) and cheap processing costs (15%). At the same time, the vast majority of bank users (64%) are willing to adopt digital-only banks for their convenience and technology utilization.
One reason behind the rise of neobanks is the change in the regulatory landscape since a global financial crisis a decade ago. Nowadays, governments have adjusted the regulators to facilitate the growth of startup banks by reducing strict procedures and heavy documents. The 2012 Financial Services Act in the UK has been the most significant. In addition, many legacy banks are opening up their application programming interfaces (APIs) for fintech and third-party app development and the flexibility in integrating Bitcoin exchanges or implementing the Ripple blockchain payment mechanism. These qualities allow innovative solutions – such as digital-only banks – to be developed more quickly, attracting more clients, especially millennials and the GenZ population.
Among the digital-only banks, Nubank is the world’s most valuable It has grown into a diversified financial services firm since launching its first product, the Nu Credit Card, in 2014. It is based in Sao Paulo and provides solutions that assist clients in spending, saving, borrowing, and investing.
Another successful neobank is Revolut – one of the most widely used digital banks in Europe. Revolut offers banking services such as prepaid debit cards (MasterCard and Visa), currency exchange, cryptocurrency exchange, and peer-to-peer payments. Its mobile app enables spending and ATM withdrawals in up to 120 currencies, as well as allows the exchange of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC), Bitcoin Cash (BCH), Litecoin (LTC), Ethereum (ETH), and XRP to or from 25 fiat currencies.

In 2021, the company became U.K.’s most valuable fintech at roughly $33 billion. Six years since its launching, Revolut has attracted more than 18 million users, who make around 150 million transactions each month.
Adopting digital-only banking: Opportunities and Challenges
Many potential customers have shifted to digital banking habits. The phenomenon is gaining traction as mobile devices become ubiquitous as Gen Y and Gen Z enter the consumer market. Nearly 300 banking-related digital interactions occur from each client, with 70% on a mobile device. Internet banking usage has increased because of lockdown restrictions, with 80% of consumers preferring it over going to the brick-and-mortar bank.
Yet, the greatest opportunity for the banking industry from the rising trend of digital-only banks is better market predictions. Digital banking is underpinned by an accurate data collection system, which AI mainly facilitates. By analyzing customer data on their financial behavior and interests, banks and financial institutions can forecast the market and provide better customer service.

However, the rise of digital banking can pose some challenges for both customers and financial service providers in terms of cybersecurity and human resource improvement. In 2020, a considerable increase in consumers’ use of mobile applications and websites for financial transactions made it a prime target for hackers. Notably, 1,506 incidents involving customer data were reported within the US. According to the Deloitte Center for Financial Services Global Outlook Survey 2020, 71% of bank executives expect their organizations to increase cybersecurity spending. Cloud computing/storage and data privacy are the top 3 areas where improvements are needed to combat the risk of data breaches.
In addition, the banking industry must keep the staff’s expertise at the same pace as technological advancements. Once the workforce fully understands and is capable of managing related technology, they can secure their positions and make the most of the advantages, like utilizing the analysis property in reporting and planning.
In Summary
Digital-only banks are a definite rising trend around the world. Benefitting from customers’ shift towards digital services and fast-growing technology, they deliver widely popular virtual services with minimum expenses while revolutionizing the industry through data analysis and market predictions. Yet, both customers and banks should be aware of the cybersecurity risks and the need to improve the workforce’s expertise considering the changes technology can make to the whole industry.
Drive innovation in banking and finance with us
Are you looking to stay ahead in the evolving financial landscape? Do you wish to stand out with a cutting-edge solution? Our expertise ensures seamless integration, robust security, and exceptional user experiences.
Leave your contact details below to discover how our services can propel your digital banking initiatives.
Error: Contact form not found.






